Hepatitis, an inflammation of the liver, is a serious health concern worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hepatitis B and C affect over 325 million people globally, causing 1.4 million deaths annually.
Hepatitis, an inflammation of the liver, is caused by various factors, including viral infections, alcohol use, and certain medications. Despite its prevalence, there are many misconceptions about hepatitis.
Common Misconceptions
1. Hepatitis is always caused by alcohol
FACT: While excessive alcohol consumption can lead to hepatitis, most cases are due to viral infections (hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E). Other causes include medications, autoimmune diseases, and other infections.
2. All types of hepatitis are the same
FACT: There are several types of hepatitis, each caused by different viruses and with different modes of transmission and impacts on health. Hepatitis A is usually acute and self-limiting, while hepatitis B and C can become chronic and lead to serious complications.
3. Hepatitis B and C are only spread through sexual contact
FACT: Hepatitis B and C can be transmitted through blood and body fluids. This includes sharing needles, unsanitary tattoo or piercing equipment, and from mother to child during childbirth. Sexual transmission is possible but not the only route.
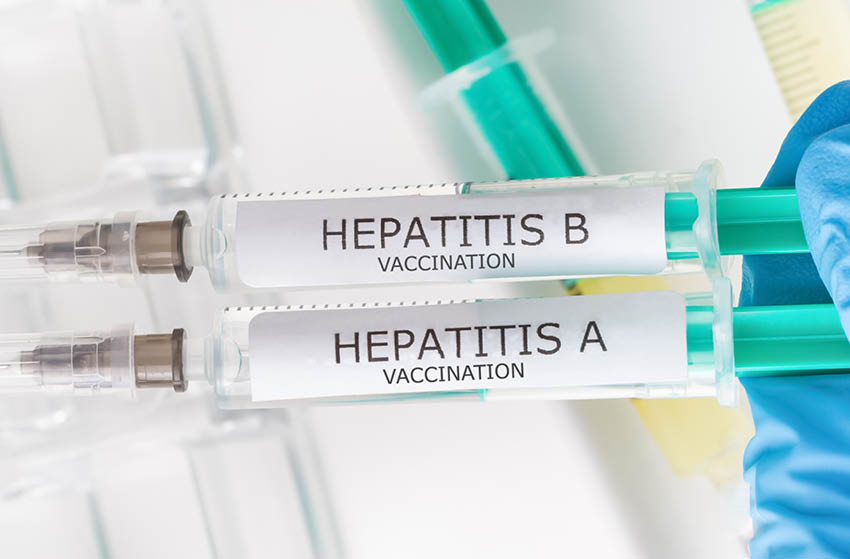
4. Vaccines are available for all types of Hepatitis
FACT: Vaccines are available for hepatitis A and B. However, there are no vaccines for hepatitis C, D, or E. Prevention for these types relies on other methods like safe injection practices and screening of blood products.
5. People with Hepatitis cannot live normal lives
FACT: With proper medical care and lifestyle adjustments, people with hepatitis can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. Chronic hepatitis B and C can be managed with antiviral medications and regular monitoring.
Living with it
- Regular Medical Care
Regular visits to a healthcare provider are crucial. They can monitor liver function, screen for complications, and adjust treatment plans as needed. - Healthy Diet:
Eating a balanced diet supports liver health. Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and avoid excessive alcohol and fatty foods. - Avoid Alcohol and Certain Medications:
Alcohol can further damage the liver. Some medications, including over-the-counter drugs, can also harm the liver. Always consult with a healthcare provider before taking new medications. - Exercise:
Regular physical activity helps maintain overall health and can improve liver function. - Vaccinations:
Vaccines for hepatitis A and B are recommended, especially if you are at higher risk for these infections. - Mental Health Support:
Living with a chronic illness can be stressful. Seeking support from counselors or support groups can be beneficial.
Prevention
- Vaccination:
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B. These vaccines are highly effective and safe.
- Safe Practices:
- Avoid sharing needles, razors, toothbrushes, or any items that might come into contact with blood.
- Ensure tattoos and piercings are done with sterile equipment.
- Safe Sex:
- Use condoms and get tested regularly if you are sexually active with multiple partners. Open communication with partners about STI status is essential.
- Good Hygiene:
- Hepatitis A is transmitted through contaminated food and water. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially after using the restroom and before eating.
- Travel Precautions:
- If traveling to areas where hepatitis A or E is common, avoid drinking tap water and eating raw or undercooked foods.
- Screening and Blood Safety:
- Blood donations and organ transplants should always be screened for hepatitis. If you are in a high-risk group, regular screening can help with early detection and management.
The Situation in Nigeria
Nigeria faces a significant hepatitis burden. The WHO estimates that about 19 million Nigerians live with hepatitis B, and 2.2 million with hepatitis C Challenges include limited access to healthcare, low awareness, and insufficient vaccination coverage.
Key measures in Nigeria include:
- Enhanced Vaccination Programs:
- Increasing vaccination rates for hepatitis B, particularly among newborns.
- Improved Healthcare Access:
- Expanding access to testing and antiviral treatments.
- Public Education Campaigns:
- Raising awareness about transmission, prevention, and the importance of early diagnosis.
- Safe Medical Practices:
- Ensuring the use of sterile equipment in healthcare settings to prevent spread.
Understanding hepatitis, debunking myths, and promoting prevention are critical in tackling this global health concern. Individuals can effectively treat hepatitis with appropriate medical care, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures. In Nigeria, raising awareness and providing access to healthcare services are critical measures in reducing the hepatitis burden.