Despite undergoing a major rebasing of its Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Nigeria has retained its position as the fourth-largest economy in Africa, according to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS).
The rebasing, which updated the base year from 2010 to 2019, expanded Nigeria’s GDP to ₦372.8 trillion (approximately $243 billion) for the year 2024—up from ₦314.02 trillion in the previous year. The exercise, covering the period from 2019 to 2023, incorporated structural changes, improved sectoral data, and a broader coverage of the informal economy.
While the revised figures reflect a 30 percent growth above the International Monetary Fund (IMF)’s earlier projection of $188 billion, Nigeria still falls short of reclaiming its former top spot on the continent.
South Africa currently leads as Africa’s largest economy with a GDP of $410.34 billion, despite having a significantly smaller population. Egypt ranks second with $347 billion, followed by Algeria at $268.9 billion.
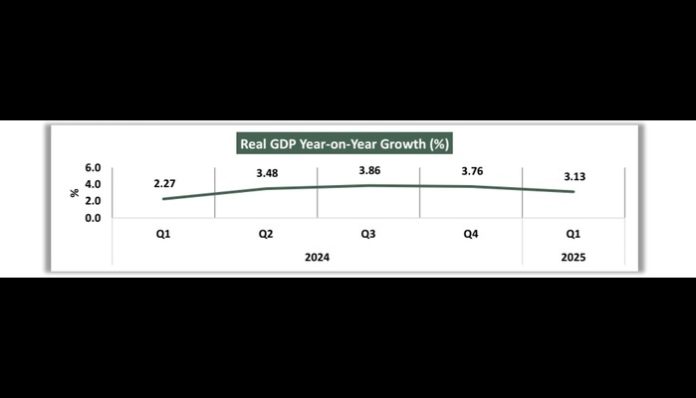
In a related development, Nigeria’s economy recorded a 3.13 percent growth rate in the first quarter of 2025, an improvement from the 2.27 percent growth recorded in the same period last year. This growth was largely driven by the services sector, which contributed 57.5 percent to the country’s aggregate GDP. The industry and agriculture sectors followed, with growth rates of 3.42 percent and 0.07 percent, respectively.
According to the NBS, the country’s aggregate GDP at basic prices stood at ₦94 trillion in nominal terms in Q1 2025—an 18.3 percent year-on-year increase compared to ₦79 trillion recorded in the first quarter of 2024.
The rebasing exercise aligns Nigeria’s GDP measurement with international standards, offering a more accurate reflection of the economy’s current structure and sectoral contributions.